Cyber threats are escalating in sophistication, affecting businesses across all sectors. Despite a common belief among small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) that their size makes them less attractive targets, attackers often focus on them due to comparatively weaker security measures. In fact, recent data highlights this vulnerability. According to a report by BusinessDasher, 43% of cyber attacks target small businesses, and 60% of those affected shut down within six months.
It requires a structured, proactive approach to managing cybersecurity risks. The truth is that a well-defined cybersecurity plan enables businesses to identify potential threats, implement appropriate safeguards, and respond effectively to security incidents. Achieving cyber readiness involves more than just installing antivirus software or performing data backups.
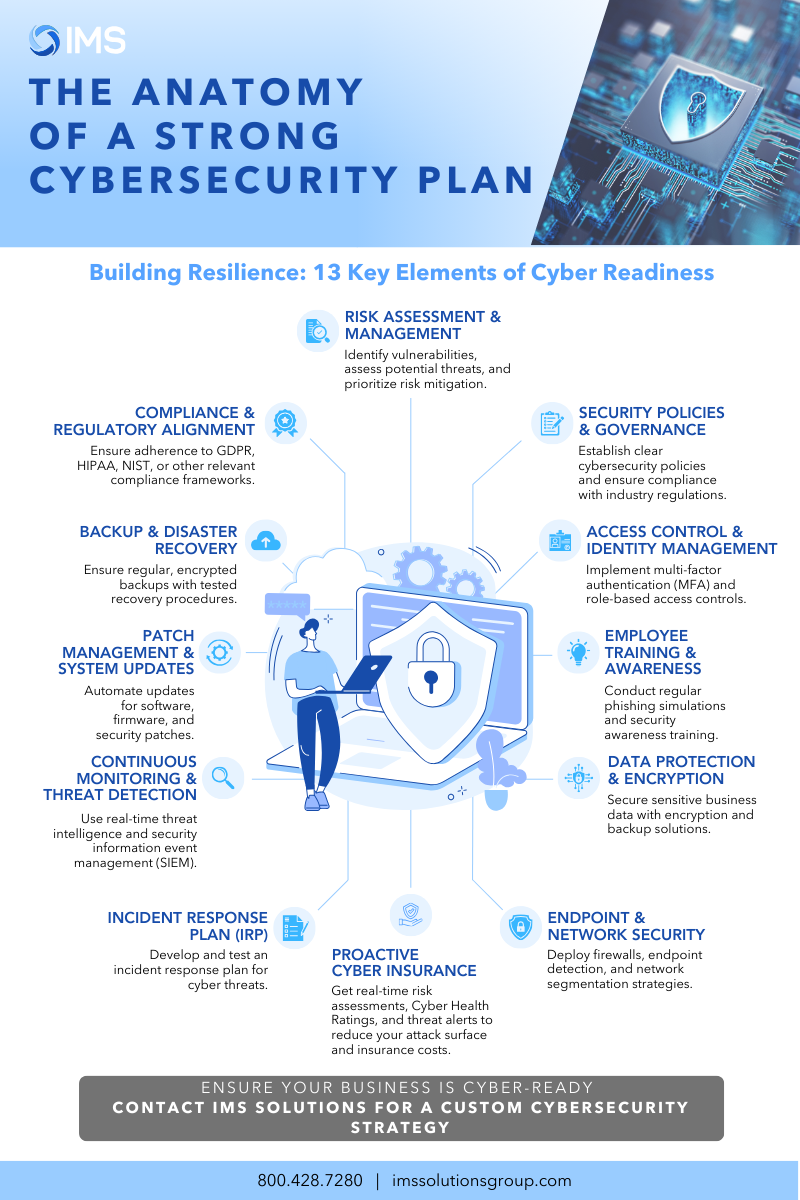
In this blog, we outline 13 key steps to help you develop cyber-readiness and establish a resilient security framework for your organization.
1. Cyber Readiness & Risk Mitigation
Cyberattacks cost businesses millions each year, with SMBs often facing disproportionate losses due to downtime, legal fees, and lost customer trust. Investing in cyber readiness helps businesses strengthen defenses before an attack occurs.
- Financial impact of cyber incidents – According to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average data breach costs $4.45 million. While SMBs may not face losses on this scale, even a fraction of that amount can be devastating. Many small businesses struggle to recover from the operational and financial strain.
- Reducing vulnerabilities – Cybercriminals target weak points such as outdated software, poor password policies, and untrained employees. Addressing these gaps through cyber-readiness strategies minimizes risk and strengthens overall security.
- Legal and regulatory considerations – Non-compliance with cybersecurity regulations can result in significant fines. Businesses that implement risk mitigation strategies can avoid penalties while protecting sensitive customer and financial data.
Preventative measures are always more cost-effective than recovering from an attack. Prioritizing cyber readiness not only strengthens security but also protects business continuity and long-term stability.
2. Risk Assessment and Management
Without a clear assessment, businesses may overlook vulnerabilities that put operations and sensitive data at risk. A structured risk assessment identifies security gaps, helping businesses make informed decisions about protecting their systems.
- Identify critical assets – Determine which systems, applications, and data are essential to daily operations. Prioritizing high-value assets ensures security measures focus on protecting what matters most.
- Assess potential threats – Cyber risks come from various sources, including cybercriminals, insider threats, and system failures. Understanding these threats helps businesses develop targeted defense strategies.
- Evaluate security gaps – Weaknesses in networks, outdated software, and poor access controls create opportunities for cyberattacks. Identifying and addressing these gaps reduces exposure to security breaches.
- Prioritize risks effectively – Not all threats pose the same level of risk. Assessing potential impact and likelihood ensures resources are allocated where they are needed most.
Regular risk assessments keep cybersecurity strategies aligned with evolving threats. Cyber readiness depends on staying proactive, identifying new risks, and continuously improving security measures.

3. Security Policies and Governance
Strong security policies provide clear guidelines on how employees, contractors, and third parties handle business data and IT systems. Establishing a structured governance framework helps ensure accountability and reduces the risk of human error.
- Acceptable use and authentication policies – Define how employees should use company devices, networks, and applications. Enforce password guidelines and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to strengthen access security.
- Data classification and handling – Categorize sensitive information based on risk levels and establish clear procedures for storage, transmission, and disposal to prevent unauthorized access.
- Incident response planning – Outline step-by-step actions for identifying, containing, and recovering from cyber incidents. Regularly test response plans to improve readiness.
A well-structured cybersecurity policy not only strengthens compliance but also helps businesses respond effectively to threats. Cyber readiness starts with clear expectations and consistent enforcement of security practices.
4. Access Control and Identity Management
No proper identity and access controls allows attackers or insiders to exploit sensitive data and critical systems. Restricting access based on job roles helps reduce exposure to potential threats.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) – Assign access permissions based on job responsibilities, ensuring employees can only access the data and systems they need to perform their duties.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) – Require additional authentication layers, such as a one-time code or biometric verification, to strengthen security beyond just passwords.
- Regular access reviews – Periodically audit user permissions to remove unnecessary access and promptly disable accounts when employees change roles or leave the company.
Effective access management reduces security risks while maintaining operational efficiency. Cyber readiness depends on protecting sensitive data with strong access controls and proactive identity management.
Want to See How Cyber Hygiene Shapes Access Security? Explore our checklist for financial institutions—packed with actionable tips to help you enforce smarter controls, improve user oversight, and tighten identity management.
Click below to read The Essential Cyber Hygiene Checklist for Financial Institutions in 2025.
5. Employee Training and Awareness
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Cyber readiness depends on equipping staff with the knowledge to recognize and respond to potential threats.
- Identifying phishing and social engineering – Attackers use deceptive emails, calls, and messages to trick employees into revealing sensitive information. Regular phishing simulations and awareness campaigns help staff recognize and avoid these tactics.
- Strengthening password security – Weak passwords and reuse across accounts create security gaps. Encourage employees to use strong, unique passwords and implement password managers to simplify secure credential storage.
- Reporting and response protocols – Employees should know how to report suspicious activity and respond to potential security incidents. Clear reporting structures reduce response time and minimize damage.
Ongoing training ensures cybersecurity remains a priority, rather than a one-time initiative. A well-informed workforce significantly reduces the risk of human error leading to security breaches.
6. Data Protection and Encryption
Unauthorized access, accidental leaks, and cyberattacks can all compromise business information. Cyber readiness includes encryption and strict data handling policies to prevent exposure.
- Encrypting stored and transmitted data – Encryption scrambles data so that only authorized users can read it. Businesses should encrypt data on servers, laptops, and mobile devices, as well as secure communications like emails and file transfers.
- Restricting data access – Not all employees need access to all information. Limit permissions based on job roles and ensure only authorized individuals can view or modify sensitive files.
- Using secure backups – Data loss can occur due to cyberattacks, hardware failures, or accidental deletions. Regularly back up encrypted copies of critical data and store them in secure locations to ensure recovery when needed.
A strong data protection strategy minimizes the risk of breaches and helps businesses maintain compliance with security regulations. Encryption and access controls add critical layers of defense against cyber threats.

7. Endpoint Protection
Cyber threats often exploit vulnerable devices, making endpoint security a critical aspect of cyber readiness. Strengthening endpoint protection ensures that workstations, laptops, and mobile devices remain secure, even in remote environments.
- Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools – These solutions continuously monitor devices for suspicious activity, allowing businesses to detect and contain threats before they spread. EDR also provides real-time insights into potential security gaps.
- Enforce strict device security policies – Require employees to keep software updated, use company-approved security applications, and follow guidelines for handling sensitive data. Restricting the use of unauthorized apps and USB devices helps prevent security risks.
- Enable remote device management – Businesses should have the ability to track, update, and secure company devices no matter where they are used. Remote wiping ensures lost or stolen devices don’t become security liabilities.
Well-protected endpoints reduce the risk of cyber incidents and help maintain business continuity. Cyber readiness starts with securing every device that connects to company networks.
8. Network Security
Cybercriminals often exploit poorly secured networks to steal sensitive information or disrupt business operations. Strengthening network defenses protects both internal systems and remote connections.
- Configure firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) – Firewalls filter incoming and outgoing traffic to block malicious activity, while IPS solutions detect and stop potential threats before they cause damage. Both help keep networks secure from external attacks.
- Use virtual private networks (VPNs) for remote access – VPNs encrypt internet traffic, making it difficult for attackers to intercept sensitive data. This is especially important for employees working outside the office or accessing company resources from public networks.
- Segment networks to limit exposure – Keeping guest Wi-Fi separate from internal systems prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive business information. Limiting network access based on role reduces the potential attack surface.
Proactive network security measures strengthen cyber readiness and prevent costly security breaches. A well-protected network ensures businesses can operate without unnecessary risk.

9. Incident Response Plan (IRP)
Even with strong defenses, security incidents can still happen. A well-structured incident response plan (IRP) helps businesses contain threats, minimize damage, and restore operations quickly.
- Defined roles and responsibilities – Establish a response team with specific tasks for identifying, containing, and mitigating threats. Clarity in roles ensures swift action when an incident occurs.
- Clear communication protocols – Outline how and when to notify stakeholders, customers, and regulatory bodies. Timely and accurate communication prevents misinformation and protects business reputation.
- Structured recovery and prevention steps – Document procedures for restoring systems, analyzing the root cause, and strengthening defenses to prevent similar incidents in the future. Regular updates to the plan ensure relevance against evolving threats.
Testing and refining the IRP regularly strengthens cyber readiness and reduces the risk of prolonged downtime. A proactive response strategy protects both business operations and customer trust.
10. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Without proactive oversight, businesses risk missing early warning signs that could prevent a security breach. Implementing continuous threat detection strengthens cyber readiness and reduces exposure to potential threats.
- Automated alerts for unusual activity – Set up real-time notifications for unauthorized access, failed login attempts, and suspicious file modifications. Early detection allows immediate action before damage spreads.
- Security log analysis for threat patterns – Review system logs to identify anomalies that indicate possible cyberattacks. Recognizing trends helps refine security policies and prevent recurring issues.
- 24/7 monitoring with expert support – Partner with a managed security provider to ensure round-the-clock surveillance and rapid response to emerging threats. External expertise enhances detection capabilities without adding internal workload.
Continuous monitoring keeps businesses one step ahead of attackers and strengthens long-term security. A well-monitored environment ensures quick responses and minimizes the risk of undetected breaches.

11. Patch Management and System Updates
Outdated software creates security gaps that cybercriminals exploit. Many attacks succeed because businesses delay or overlook updates, leaving known vulnerabilities exposed. Staying on top of patches strengthens cyber readiness and reduces the risk of breaches.
- Automate updates – Enable automatic updates to ensure critical security patches are applied without delays.
- Conduct routine audits – Regularly review and audit systems to verify that all software, firmware, and applications are up to date.
- Track your assets – Maintain an inventory of all devices and software to track update status and prevent overlooked vulnerabilities.
Consistently updating systems prevents attackers from exploiting known weaknesses. A proactive approach to patch management strengthens defenses and minimizes security risks.
12. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Data loss can occur due to cyberattacks, system failures, or unexpected disruptions. Without a solid backup and recovery plan, businesses risk prolonged downtime and financial losses. Cyber readiness includes ensuring data remains protected and accessible when needed.
- Diversify storage locations – Store backups both offline and in the cloud to prevent ransomware from compromising all copies.
- Test regularly – Test backups regularly to confirm that data can be restored without errors or delays.
- Document recovery steps – Document clear recovery procedures so employees know the steps to follow after an incident.
A well-planned backup strategy safeguards business continuity and prevents disruptions. Reliable data recovery ensures operations can resume quickly, minimizing the impact of unexpected events.
13. Cyber Insurance
A proactive “Active Insurance” approach helps SMBs combat cyber threats before they occur. This involves several key components:
- Real-time cyber risk assessment – Leverage Cyber Risk Assessments to identify vulnerabilities based on a company’s digital footprint. Our platform offers a real-time, external view of cyber risk with customized recommendations.
- Cyber Health Rating – Calculate a real-time security score (Cyber Health Rating) that evaluates an organization’s cybersecurity posture based on key risk indicators such as attack surface vulnerabilities and threat intelligence data.
- Technology integration – Implement scanning technologies to assess potential vulnerabilities, mirroring how cybercriminals think. We also develop a marketing technology stack to streamline and measure persona-targeted campaigns.
By combining continuous monitoring, risk assessments, targeted alerts, and actionable guidance, our aim is to actively reduce the likelihood and impact of cyberattacks on SMBs.
Ensure Your Business is Cyber Ready
Cyber readiness is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment. A well-structured cybersecurity plan helps SMBs reduce risk, protect critical data, and maintain business continuity.
IMS Solutions helps businesses in South Carolina assess their cybersecurity posture and strengthen their defenses. Contact our team for a cyber audit or consultation to ensure your business is prepared for today’s threats.