Cyber threats have shown no signs of slowing down as we progress through the first month of 2025. Financial institutions remain high-priority targets for cybercriminals, with ransomware attacks and state-sponsored activities continuing to disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data.
In fact, recent reports indicate that ransomware alone accounted for nearly 25% of all cyber incidents in the financial sector last year, underscoring the urgent need for proactive measures. As a decision-maker responsible for your institution’s cyber security services, how prepared are you to address these evolving threats?
With cyber threats growing, most businesses—even financial institutions—struggle to stay secure. In this short video, Tim Morrissey from IMS Solutions highlights why cyber hygiene is essential and how a few key actions can drastically improve your security posture.
The recent CSBS Cyber Hygiene Memo outlines practical steps you can take to strengthen your defenses. This blog will break down those recommendations and provide actionable insights into how foundational cyber hygiene practices can help you. By prioritizing these measures, you can position your organization to better withstand the challenges ahead while safeguarding your reputation and operations.
Why Cyber Hygiene Matters Now More Than Ever
The CSBS memo paints a clear picture: ransomware remains a significant threat, and geopolitical tensions add another layer to the complexity. Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated, not just encrypting data but stealing it as well. This means that even if you pay a ransom, your institution could still face reputational damage and regulatory fines from compromised customer information.
State-sponsored actors are also a growing concern. They engage in espionage, disrupt operations, and aim to cause widespread chaos. Financial institutions are attractive targets for these actors due to the sensitive data they hold and their critical role in the economy.
The good news? Strong cyber hygiene practices can significantly reduce your risk. Think of it as the digital equivalent of washing your hands – a simple but effective way to prevent the spread of germs. In the same way, consistent cyber hygiene can stop most cyberattacks before they even start.
10 Cyber Hygiene Practices to Protect Your Business
We’ve established that ransomware, data exfiltration, and state-sponsored attacks are serious threats to financial institutions. But how exactly can you protect your organization and your customers?
We’ve outlined below the ten fundamental cyber hygiene practices from the CSBS memo that form the foundation of a strong security posture. These are actionable steps you can take today to significantly strengthen your defenses. Let’s explore each practice in detail and see how you can implement them effectively within your business.
1. Track IT Assets
Maintain a detailed inventory of all devices and software connected to your network. This includes everything from laptops and servers to mobile devices and cloud applications. You can’t protect what you don’t know you have!
- Implement an asset management system that automatically discovers and tracks all devices and software on your network. This will help you maintain an accurate and up-to-date inventory.
- Regularly review your asset inventory to identify any unauthorized or unknown devices. Remove or remediate any devices that pose a security risk.
2. Apply Updates
According to a recent report from Ponemon Institute, over 60% of data breaches involve vulnerabilities for which a patch was available but not applied. This highlights the critical importance of keeping your systems up-to-date. Software and hardware vulnerabilities are entry points for cybercriminals. Implement a robust patch management program to keep your systems current and close those security gaps.
- Establish a regular patching schedule and automate the process wherever possible. This will help you ensure that patches are applied promptly.
- Prioritize patching critical systems and applications that handle sensitive data. Conduct thorough testing before deploying patches to production environments.
3. Replace Old Systems
Unsupported systems are easy targets. Establish an end-of-life management program to identify and replace outdated hardware and software before they become liabilities.
- Create an inventory of all software and hardware, noting their end-of-life dates. This will help you proactively plan for upgrades and replacements.
- Develop a process for securely decommissioning old systems. Ensure that all sensitive data is properly erased before disposing of or repurposing old hardware.
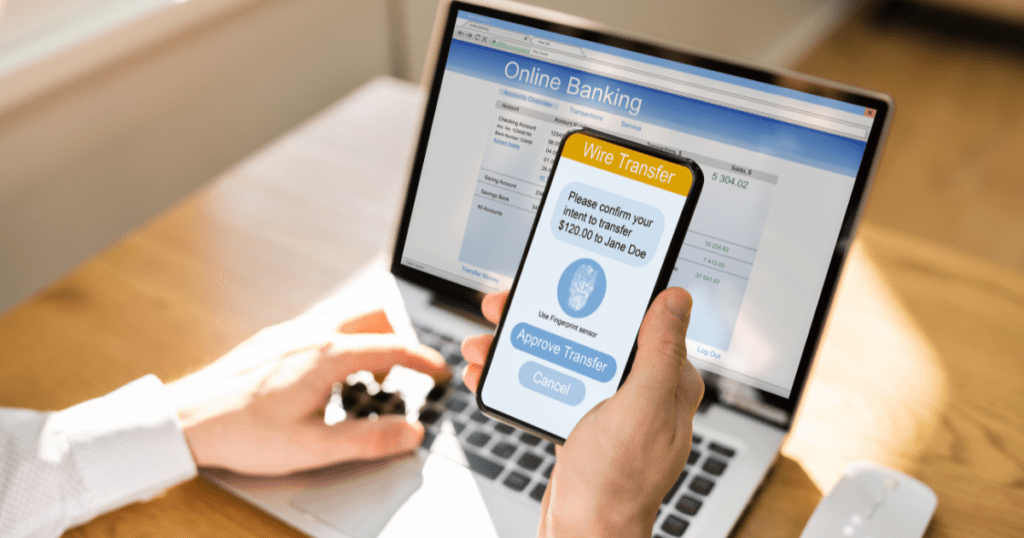
4. Secure Access
Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are your first line of defense. According to Microsoft, MFA can block over 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
- Require strong, unique passwords for all user accounts and enforce regular password changes. Consider using a password manager to help users generate and store secure passwords.
- Implement MFA for all forms of access, including remote access, VPNs, and cloud applications. Consider using phishing-resistant MFA methods like hardware tokens or biometrics.
5. Audit Vendors
Developing strong relationships with your technology vendors is essential, but it’s equally important to ensure they prioritize cyber security services as much as you do. A comprehensive third-party risk management program helps you assess and manage the security posture of all your vendors, including trusted partners like IMS Solutions.
- Conduct thorough due diligence before onboarding new vendors. Assess their cybersecurity practices and ensure they align with your institution’s standards.
- Regularly review and monitor the security posture of your existing vendors. Include security requirements and obligations in your vendor contracts.
6. Log Activities
Enable detailed logging for all systems and applications. Store these logs securely in a centralized location for analysis and incident response.
- Configure your systems to log all relevant events, including user logins, file access, and system changes.
- Use a centralized log management system to collect, store, and analyze logs from all your systems. This will help you identify suspicious activity and respond to incidents more effectively.

7. Backup Data Regularly
Maintain secure and reliable backups of critical data and systems. Test your backups regularly to ensure they can be restored in case of an incident. After all, data is the lifeblood of your financial institution. Losing access to it, even temporarily, can disrupt operations, damage your reputation, and lead to significant financial losses.
- Implement a comprehensive backup strategy that includes both on-site and off-site backups.
- Regularly test your backups to ensure they are complete and can be restored successfully. Consider using different backup methods, such as full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups.
8. Train Staff
Your employees are your first line of defense in cyber security services. Implement regular cybersecurity awareness training and conduct phishing simulations to educate them about threats and best practices.
- Provide regular training on topics such as password security, phishing awareness, and social engineering. Use engaging and interactive training methods to keep employees interested.
- Conduct regular phishing simulations to test employees’ ability to identify and report phishing attempts. Use the results of these simulations to tailor your training program and address any knowledge gaps.
9. Monitor Threats and Stay Informed
Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds from organizations like FS-ISAC, FBI InfraGard, and CISA to stay up to date on the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
- Use threat intelligence to proactively identify and mitigate potential threats to your institution.
- Share threat intelligence with your staff and vendors to help them stay informed and vigilant.

10. Test Your Responses
Develop and regularly test an incident response plan. This will help you react quickly and effectively in the event of a cyberattack, minimizing damage and downtime.
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in case of a cyberattack.
- Conduct regular tabletop exercises to test your incident response plan and identify any areas for improvement.
Beyond Cyber Hygiene – Preparing for Cyber Insurance Requirements
The cyber hygiene best practices outlined above don’t just reduce risk—they also help meet cyber insurance requirements. Insurers now demand strict security measures before offering coverage, and financial institutions that fail to comply may face higher premiums or policy rejections.
In this short video, Tyler Robertson, Senior Technology Consultant at IMS Solutions, explains how three simple actions can enhance security and support cyber insurance compliance.
Watch now to ensure your institution is protected on all fronts.
Get Cyber Security Services from IMS Solutions
Cyber hygiene isn’t just a buzzword; it’s the bedrock of security for financial institutions. By implementing these practices, you’re taking proactive steps to safeguard your data and your reputation.
IMS Solutions can help you build and maintain a strong cyber hygiene program. We offer cybersecurity services tailored to the needs of financial institutions, including cyber risk assessments, backup and recovery solutions, and employee training.
Contact IMS Solutions today to discuss how we can help you strengthen your defenses and protect your financial institution from cyber threats.


